Medication adherence is a crucial aspect of healthcare that significantly impacts patient outcomes and healthcare costs. Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) play a vital role in enhancing medication adherence through various software solutions. This article explores the landscape of PBM medication adherence software, its importance, features, and strategies for implementation.
Understanding Medication Adherence
Medication adherence refers to the degree to which patients take their medications as prescribed, including timing, dosage, and frequency. Non-adherence can lead to poor health outcomes and increased healthcare costs, estimated at up to $300 billion annually in the U.S..
The Role of PBMs in Medication Adherence
PBMs serve as intermediaries between insurers, pharmacies, and patients, managing prescription drug benefits. They implement strategies and tools to improve medication adherence among members, ensuring that patients receive the full benefit of their prescribed therapies.
Importance of Medication Adherence Software
- Enhancing Patient Outcomes
- Effective medication adherence software helps monitor patient behavior, providing insights that can lead to improved health outcomes.
- Reducing Healthcare Costs
- By improving adherence rates, PBMs can help lower overall healthcare costs associated with non-adherence, such as hospitalizations and additional treatments.
Key Features of PBM Medication Adherence Software
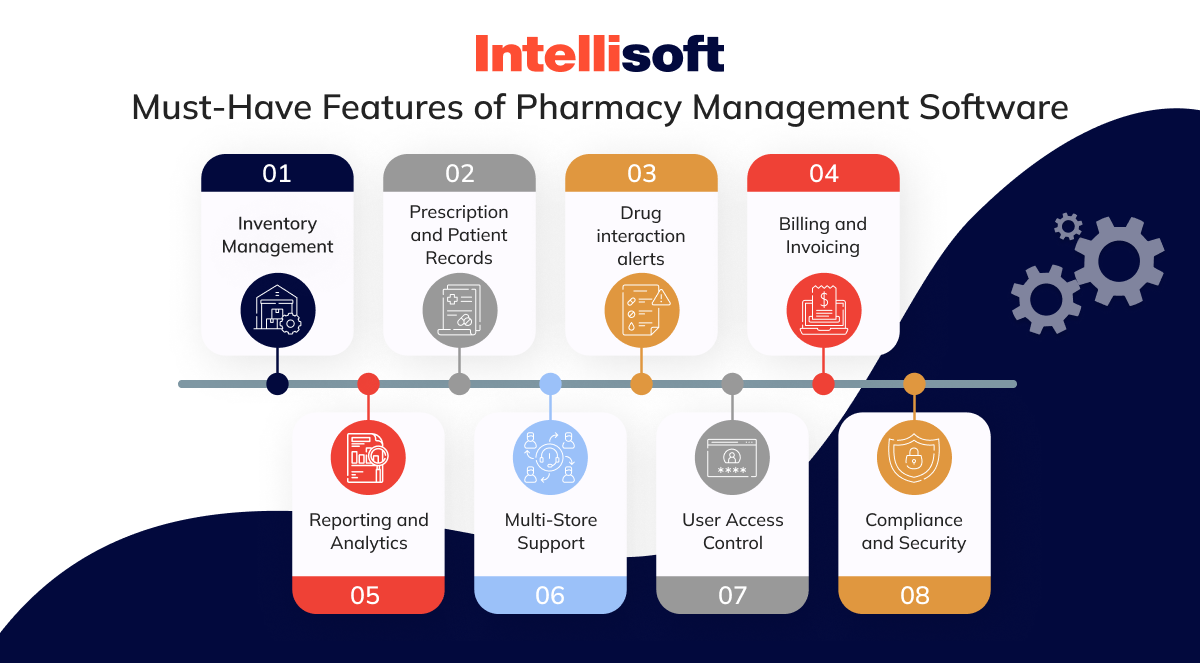
- Real-Time Monitoring
Software solutions provide real-time data on patient medication-taking behaviors, allowing for timely interventions when non-adherence is detected. - User-Friendly Dashboards
Intuitive dashboards present adherence data clearly, enabling healthcare providers to quickly assess patient compliance levels. - Alerts and Notifications
Automated alerts can notify providers or patients about missed doses or upcoming medications, facilitating better adherence practices. - Data Analytics
Advanced analytics help identify patterns in medication-taking behaviors, allowing for targeted interventions tailored to individual patient needs. - Integration with Other Systems
Effective software integrates with electronic health records (EHRs) and pharmacy management systems to streamline communication and data sharing.
Strategies for Improving Medication Adherence
1. Medication Therapy Management (MTM)
MTM involves comprehensive reviews of a patient’s medications by pharmacists to ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes. This personalized approach helps identify barriers to adherence and develop tailored action plans.
2. Academic Detailing
PBMs can analyze claims data to identify prescribing patterns that may lead to non-adherence. Educational initiatives for prescribers about cost-effective alternatives can improve adherence by making medications more affordable.
3. Personalized Member Transitions
Transitioning members between different phases of care can create gaps in medication adherence. PBMs can facilitate smoother transitions through personalized communication and support services.
4. Use of Technology
Incorporating technology such as mobile apps for medication reminders or telehealth consultations can enhance patient engagement and adherence rates.
5. Patient Education
Educating patients on the importance of their medications and how to take them correctly is fundamental in improving adherence rates. PBMs can provide resources and support to enhance patient understanding.
Challenges in Medication Adherence
Despite the availability of advanced software solutions, several challenges remain:
- Complexity of Treatment Regimens: Patients with multiple prescriptions may struggle to adhere due to complexity.
- Cost Barriers: High drug prices can deter patients from filling prescriptions.
- Lack of Symptoms: Patients may discontinue medications if they do not perceive immediate benefits.
- Communication Gaps: Insufficient communication between healthcare providers and patients contributes significantly to non-adherence.
Future Trends in PBM Medication Adherence Software
As technology evolves, so will the capabilities of medication adherence software:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can enhance predictive analytics for identifying at-risk patients.
- Wearable Devices: Integration with wearable technology could provide additional data on patient health metrics related to medication adherence.
- Enhanced User Experience: Future software will focus on user-friendly interfaces that encourage patient engagement.
Conclusion
PBM medication adherence software represents a critical tool in the fight against non-adherence. By leveraging advanced technology and implementing targeted strategies, PBMs can significantly improve patient outcomes while reducing healthcare costs.
The future holds promising advancements that will further enhance these efforts, making it imperative for stakeholders in the healthcare industry to prioritize medication adherence initiatives.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of PBM medication adherence software, its significance, features, strategies for improvement, challenges faced, and future trends shaping this essential aspect of healthcare management.
Share




