1. What is Google Indexer?
Google Indexer refers to the system that Google uses to store and organize the content of websites after they have been crawled. Once a website is crawled, the Google Indexer adds it to Google’s vast database, making it searchable. When users perform a search query, Google retrieves results from its index, not directly from the web.
2. How Does Google Indexing Work?
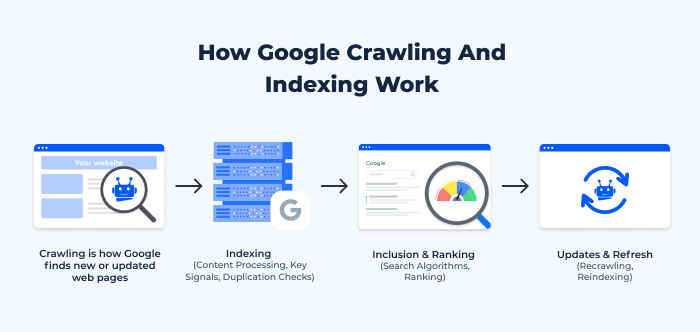
The process of Google indexing begins with crawling, where Googlebot (Google’s web crawler) discovers new or updated pages on the web. After the crawling phase, the content is analyzed, organized, and stored in Google’s index. During this process, Google looks at various factors like keywords, quality of content, and the page’s relevance to determine how it will appear in search results.
3. Crawling vs. Indexing: What’s the Difference?
- Crawling is the process where Googlebot scours the web for new and updated content.
- Indexing is the subsequent step where the discovered content is stored and organized in Google’s index for retrieval during searches.
4. Importance of Google Indexing for SEO
If your website isn’t indexed, it simply can’t appear in Google search results, no matter how well-optimized it may be. This is why indexing is one of the foundational steps for SEO. Proper indexing ensures that Google can understand your site’s content and rank it appropriately based on search queries.
5. How to Check if Your Website is Indexed

To check whether your website or a specific page is indexed, use the following steps:
- Google Search Operator: Type Rapid url indexer in Google search. If your site is indexed, it will appear in the search results.
- Google Search Console: Another method is to log into Google Search Console and check the “Coverage” report, which shows how many pages are indexed.
6. Common Issues Preventing Indexing
Several factors can prevent your pages from being indexed:
- Noindex tag: If a page has a “noindex” directive, Google will skip adding it to the index.
- Robots.txt file: Improper configuration in the robots.txt file may block Googlebot from crawling.
- Thin content: Low-quality or duplicate content may result in Google not indexing the page.
7. How to Speed Up Google Indexing
To speed up indexing:
- Submit Your Sitemap: Ensure you submit your website’s XML sitemap to Google via Google Search Console.
- Internal Linking: Use effective internal linking to help Google discover new pages.
- Fetch as Google: This tool in Search Console allows you to manually request indexing for a page.
8. Tools to Help with Indexing
- Google Search Console: Monitor your website’s indexing status and resolve any issues.
- Bing Webmaster Tools: Even though it’s for Bing, some insights from this tool may also help you with Google indexing.
- SEO Plugins (e.g., Yoast): These can help you optimize your site for easier crawling and indexing.
9. Google Indexer Best Practices
To ensure smooth and efficient indexing:
- Create Quality Content: Ensure your content is original, high-quality, and valuable to users.
- Optimize Your Site’s Structure: A well-organized site with clear navigation helps Googlebot find and index your content.
- Use Canonical Tags: Avoid duplicate content issues by using canonical tags correctly.
10. The Role of Mobile-First Indexing
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of a website for indexing and ranking. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, it may negatively impact your indexing status and rankings.
11. Google Indexer and Structured Data
Structured data (like Schema markup) can help Google better understand your content. By adding structured data, you increase the chances of rich results like snippets, knowledge panels, and more, which can enhance your visibility.
12. The Impact of Backlinks on Indexing
Backlinks from authoritative sites signal Google to crawl and index your site faster. The more high-quality backlinks you have, the more frequently Googlebot may visit your site to update its index.
13. How Often Does Google Re-Index Websites?

Google continuously re-indexes websites based on factors like content updates, backlinks, and user engagement. Some pages are crawled daily, while others may take weeks or even months for a re-crawl.
14. Can You Force Google to Index Your Site?
While you can’t “force” Google to index your site, you can use methods like:
- URL Submission in Google Search Console
- Building More Backlinks
- Promoting Content on Social Media These actions signal to Google that your site has new or updated content worth indexing.